Decimal number lines
key notes :
📍 What is a Decimal Number Line?
A decimal number line shows numbers with tenths (0.1) and hundredths (0.01) placed in order on a line.
It helps us see where decimals belong on a number line. 📏🔢
🔟➗ Decimal = Part of a Whole
Decimals show parts of a whole.
Example: 0.5 means 5 tenths (like 5/10). 🍰➡️0.5
📊 Using Tenths on a Number Line
- The space between 0 and 1 is divided into 10 equal parts.
- Each part = 0.1 (one-tenth).
Example:
0️⃣ ┃0.1┃0.2┃0.3┃0.4┃0.5┃0.6┃0.7┃0.8┃0.9┃1️⃣
💯 Using Hundredths on a Number Line
- When divided into 100 equal parts, each part = 0.01 (one-hundredth).
Example:
0.25 = 25 hundredths 🪙
📌 Marking Decimals on a Number Line
To locate a decimal:
- ✅ Find the two whole numbers it lies between
- ➗ Divide the segment into tenths or hundredths
- 📍 Mark the exact point
Example:
To find 0.6, move 6 tenths from 0.
🔄 Comparing Decimals Using Number Lines
Decimals to the right on the number line are greater ➕
Decimals to the left are smaller ➖
Example:
0.7 👉 greater than 0.4 because 0.7 is further right. ⭐
🌟 Decimal to Fraction Connection
- 0.1 = 1/10
- 0.2 = 2/10
- 0.50 = 50/100 (same as 1/2)
Decimals and fractions show the same value in different forms 🔄
🧠 Why Do We Use Decimal Number Lines?
They help us:
✅ Understand decimal values
✅ Compare and order decimals
✅ Visualize fractions and decimals together
✅ Prepare for measurement and money calculations 💵📏
🎯 Quick Example
Place 0.3 on a number line between 0 and 1:
0 ➡️ 3 jumps of 0.1 ➡️ 0.3 ✔️
Learn with an example
Find the value of t. Write your answer as a decimal number.
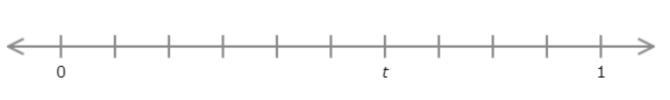
t = ______
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to t. There are 6 intervals. t is 0.6 greater than 0.
t = 0.6
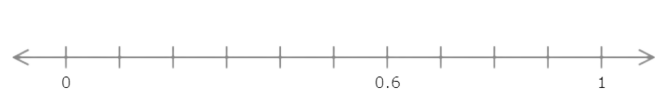
Find the value of f. Write your answer as a decimal number.
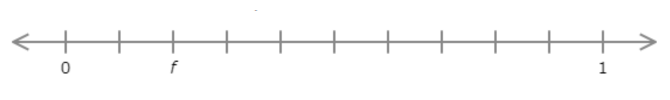
f = _____
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to f. There are 2 intervals. f is 0.2 greater than 0.
f = 0.2
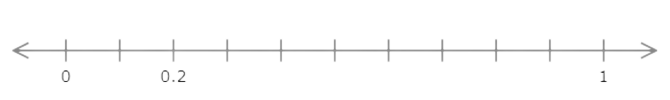
Find the value of m. Write your answer as a decimal number.
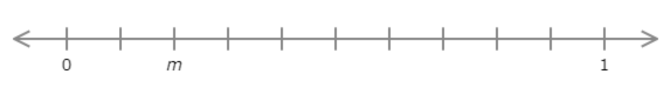
m = ______
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to m. There are 2 intervals. m is 0.2 greater than 0.
m = 0.2
Let’s practice!

