Use Venn diagrams to solve problems
Key Notes :
🔵 What is a Venn Diagram?
- A Venn Diagram is a picture with circles that show how groups (sets) are related.
- The circles may overlap to show things that belong to more than one group.
🟣🔵⚪
🟠 Parts of a Venn Diagram
- Circle A ➝ First group
- Circle B ➝ Second group
- Overlap area ➝ Items that belong to both groups
- Outside area ➝ Items that belong to none of the groups
✨ Example:
- 👟 Sports players
- 🎨 Artists
- People who do both 👟🎨 go in the overlap!
🟢 Why Do We Use Venn Diagrams?
To compare and contrast two or more groups
To organize information
To spot similarities and differences easily
To answer questions like:
- “How many like BOTH?”
- “How many like ONLY one?”
- “How many like NONE?”
📊🧠
🔴 How to Fill a Venn Diagram
Follow these steps:
1️⃣ Start with the overlap (both sets)
2️⃣ Add items that belong to only Set A
3️⃣ Add items that belong to only Set B
4️⃣ Add items that belong to neither set
5️⃣ Finally, answer the problem using your diagram
📝➡️⭕⭕➡️✔️
🟣 Example Question
20 students were asked:
- 12 like 🍎 apples
- 10 like 🍌 bananas
- 5 like both
✨ Fill the Venn Diagram:
- Put 5 in the overlap
- Only apples: 12 − 5 = 7
- Only bananas: 10 − 5 = 5
- Total who like at least one fruit: 7 + 5 + 5 = 17
- None: 20 − 17 = 3
🎉 Students learn how to compare and solve!
💡 Tips for Success
- Always fill the middle overlap first!
- Double-check totals by adding all parts
- Use Venn diagrams to solve word problems easily 💪📘
🌈 Real-Life Uses
- Sorting animals 🐶🐱
- Comparing shapes 🔺🟦
- Survey results in class 🧃🍪
- Finding common hobbies 🎵⚽
Learn with an example
1) 4 of the students in Charlotte’s class have a jacket with a hood and 6 have a jacket with buttons. 3 students have a jacket with both a hood and buttons.
How many students have a jacket with buttons but not a hood?
____ students
Make a Venn diagram to solve the problem.
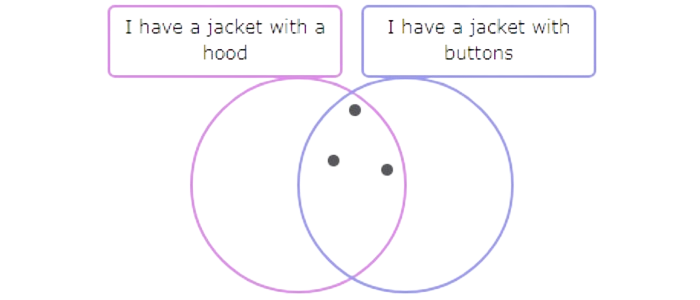
3 students have a jacket with both a hood and buttons. Put 3 dots in the area that is in both circles.
Now add dots to the other two areas until there are 4 dots in the “I have a jacket with a hood” circle and 6 dots in the “I have a jacket with buttons” circle.
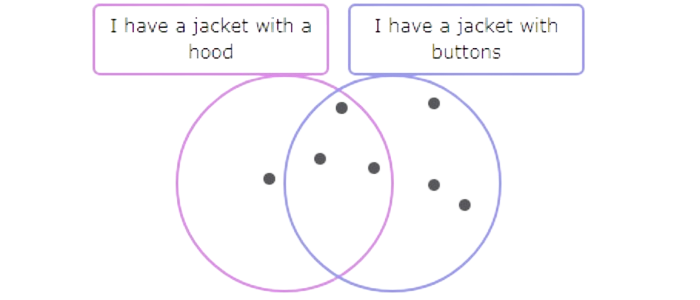
Count the dots that are in the “I have a jacket with buttons” circle but are not in the “I have a jacket with a hood” circle. There are 3 dots.
3 students have a jacket with buttons but not a hood.
2) 4 of the children in Carrie’s class have an orange marble. 3 children have a red marble, and 2 children have both an orange marble and a red marble.
How many children have a red marble but not an orange marble?
____ children
Make a Venn diagram to solve the problem.
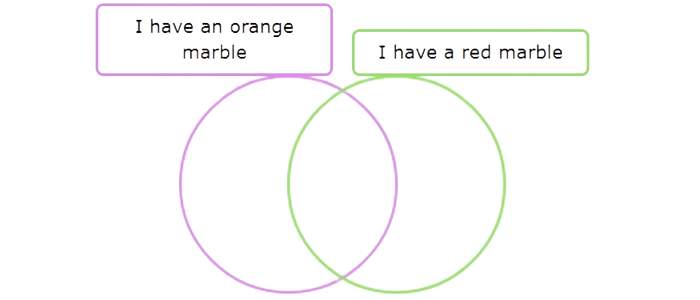
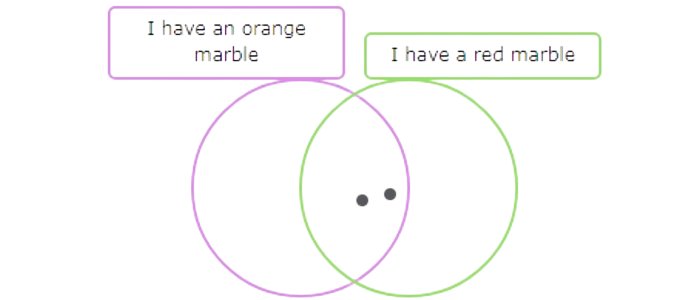
2 children have both an orange marble and a red marble. Put 2 dots in the area that is in both circles.
Now add dots to the other two areas until there are 4 dots in the “I have an orange marble” circle and 3 dots in the “I have a red marble” circle.
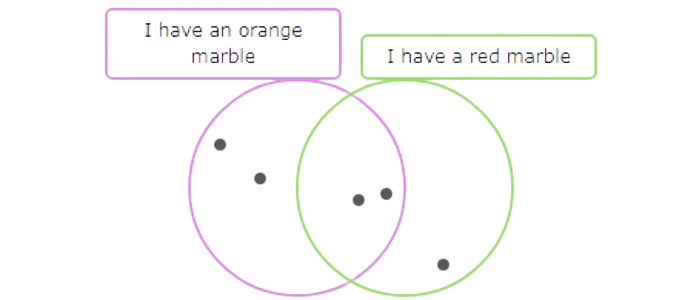
Count the dots that are in the “I have a red marble” circle but are not in the “I have an orange marble” circle. There is 1 dot.
1 child has a red marble but not an orange marble.
3) 7 of the people in Levi’s flat building like leopards and 7 like jaguars. 5 people like both leopards and jaguars.
How many people like leopards or jaguars or both?
_____ people
Make a Venn diagram to solve the problem.
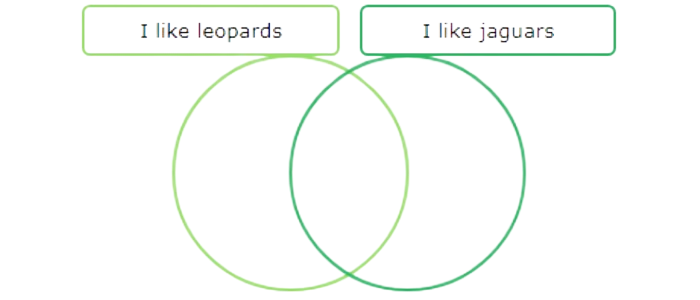
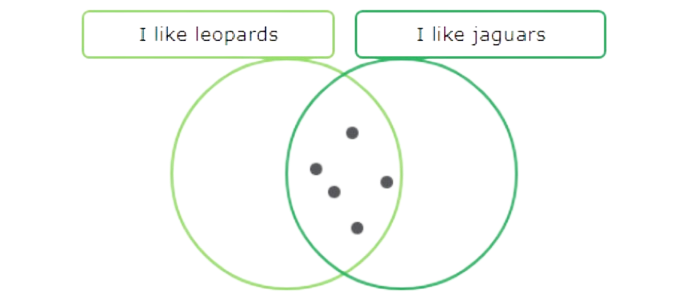
5 people like both leopards and jaguars. Put 5 dots in the area that is in both circles.
Now add dots to the other two areas until there are 7 dots in the “I like leopards” circle and 7 dots in the “I like jaguars” circle.
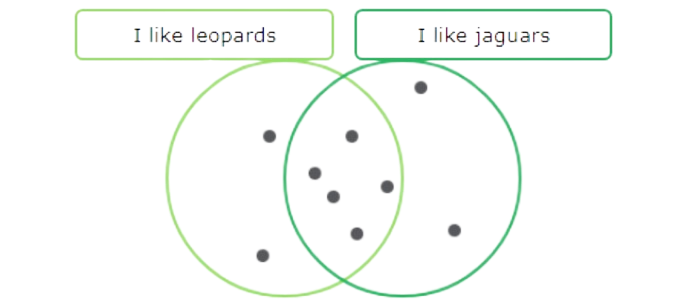
Count the total number of dots in the diagram. There are 9 dots.
9 people like leopards or jaguars or both.
Let’s practice!🖊️

