How Do Plant Reproduce?
Key Notes:
Types of Reproduction:
Sexual Reproduction:
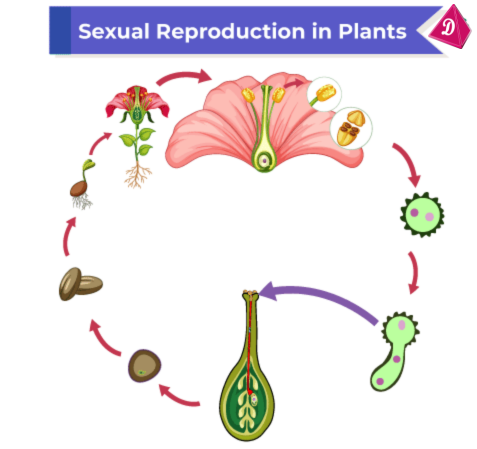
- Involves the union of male and female reproductive cells (pollen and ovule) to form seeds.
Asexual Reproduction:
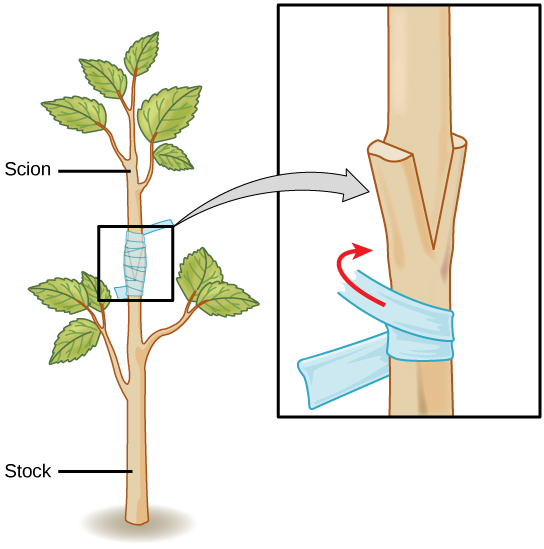
- Occurs without the involvement of seeds or spores, often using vegetative parts like stems, roots, or leaves.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants:
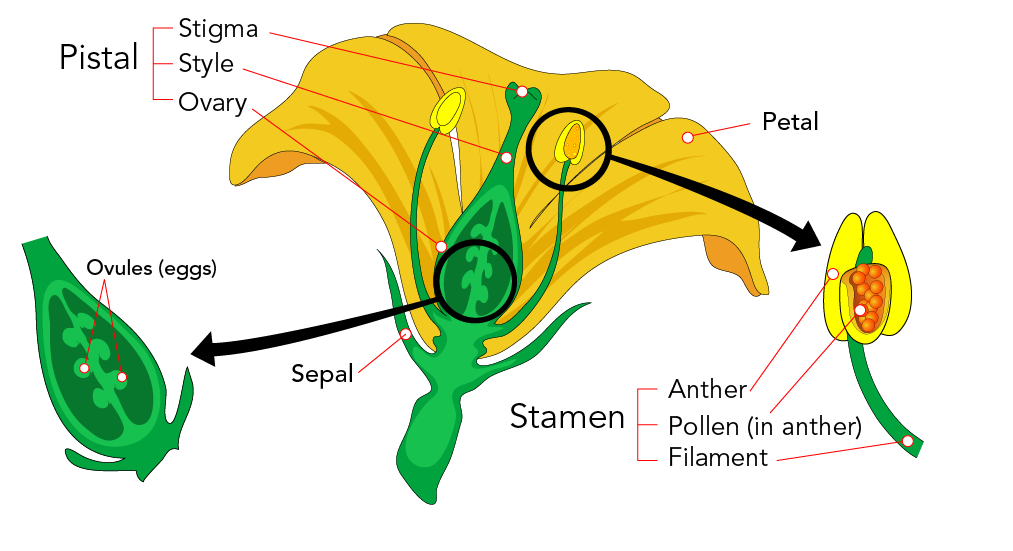
Flower Structure:
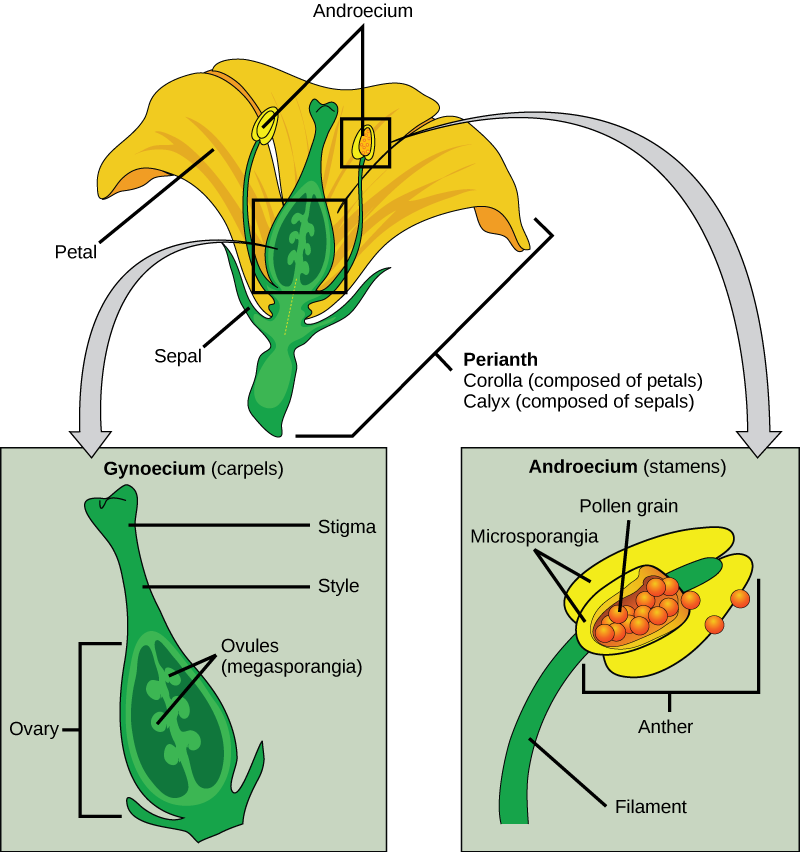
- Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms (flowering plants).
Pollination:

- Transfer of pollen from the male part (anther) to the female part (stigma) of the flower.
Fertilization:
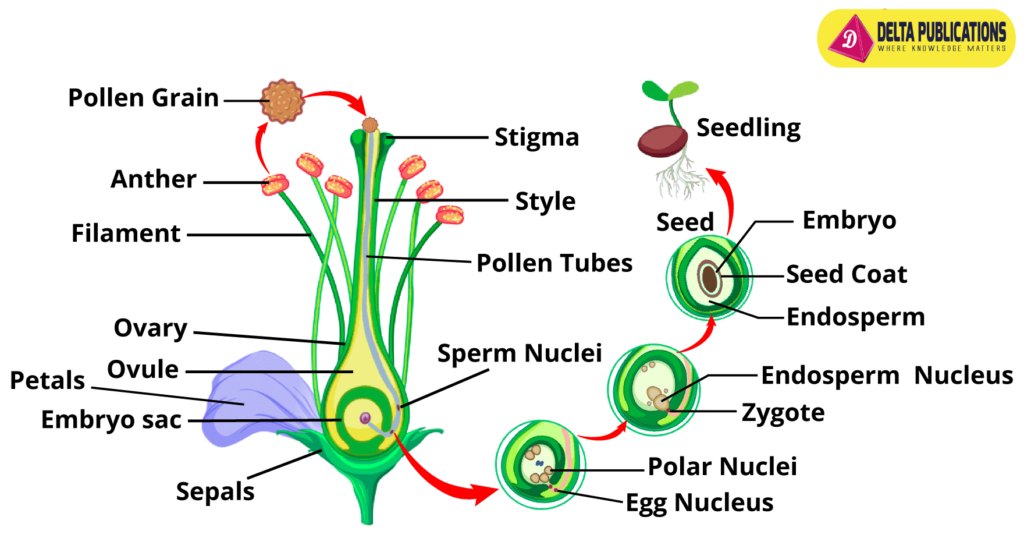
- Fusion of the male gamete (pollen) with the female gamete (ovule) inside the ovary to form a seed.
Asexual Reproduction in Plants:
- Types: Includes methods like budding, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation (runners, rhizomes, tubers, bulbs).
- Advantages: Allows rapid reproduction without the need for pollinators or the production of seeds.
Examples of Plant Reproduction:
- Sexual: Formation of seeds in flowering plants like peas, apples, and roses.
- Asexual: Growing new plants from cuttings (e.g., mint), bulbs (e.g., tulips), or runners (e.g., strawberries).
Significance of Reproduction:
- Maintaining Species: Ensures continuity of plant species and genetic diversity.
- Adaptation: Allows plants to adapt to changing environments through genetic variation.
Human Impact:
- Cultivation: Farmers use both sexual and asexual methods to propagate crops efficiently.
- Conservation: Understanding plant reproduction helps in conserving endangered plant species.
Let’s practice!

