Reproduction From Seeds
Key Notes:
Introduction to Reproduction in Plants
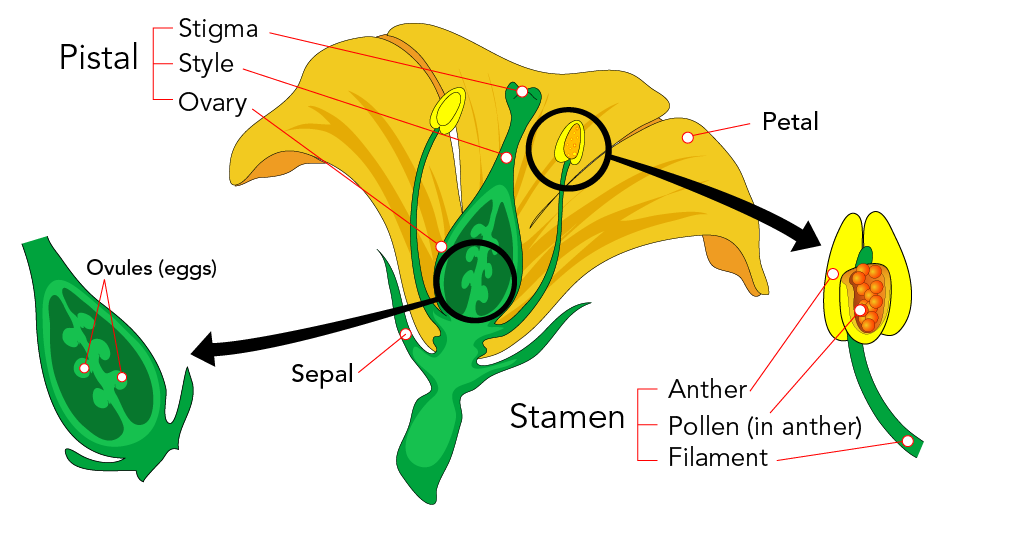
- Reproduction: The process by which plants produce new plants of the same kind.
- Seeds: The primary method of reproduction in most plants.
Parts of a Seed
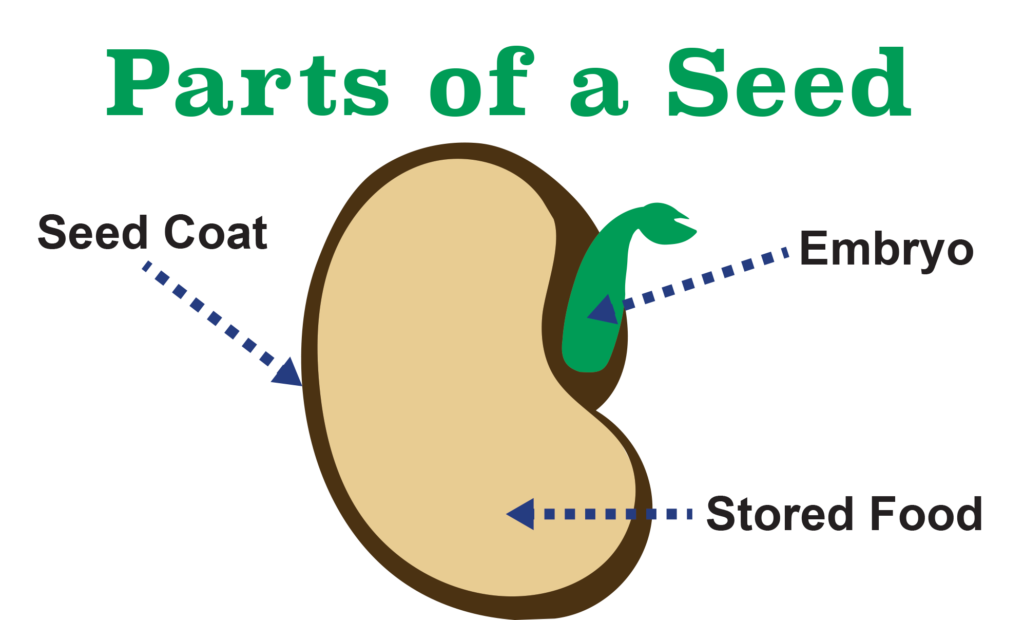
- Seed Coat: The outer protective layer of the seed.
- Embryo: The baby plant inside the seed that develops into a new plant.
- Cotyledons: Also known as seed leaves, these store food for the growing embryo.
- Endosperm: In some seeds, it serves as additional food storage.
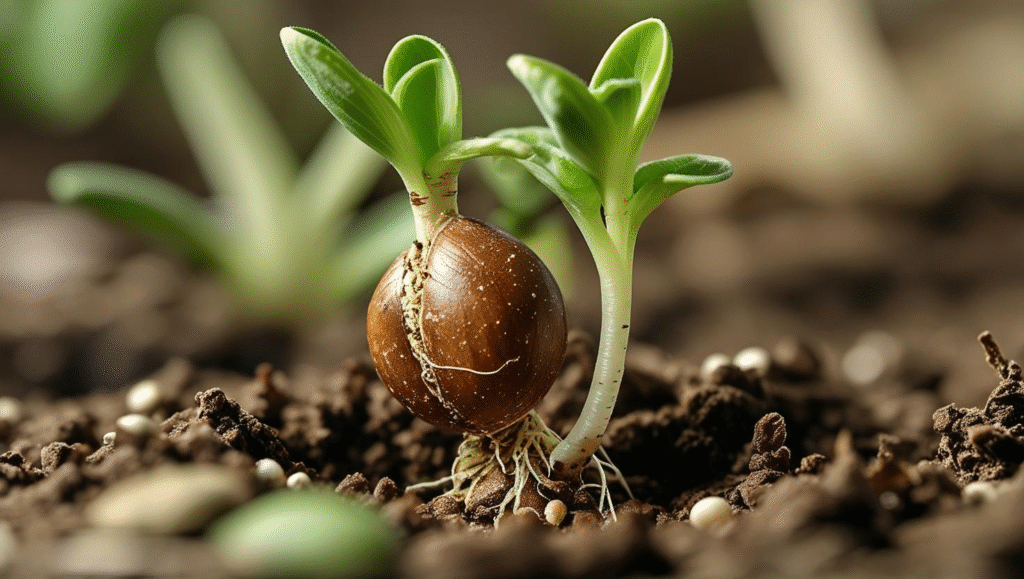
Germination Process
- Germination: The process by which a seed develops into a new plant.

Conditions for Germination:
- Water: Activates enzymes that begin the growth process.
- Oxygen: Needed for respiration during growth.
- Warmth: Necessary for the enzymes to function properly.
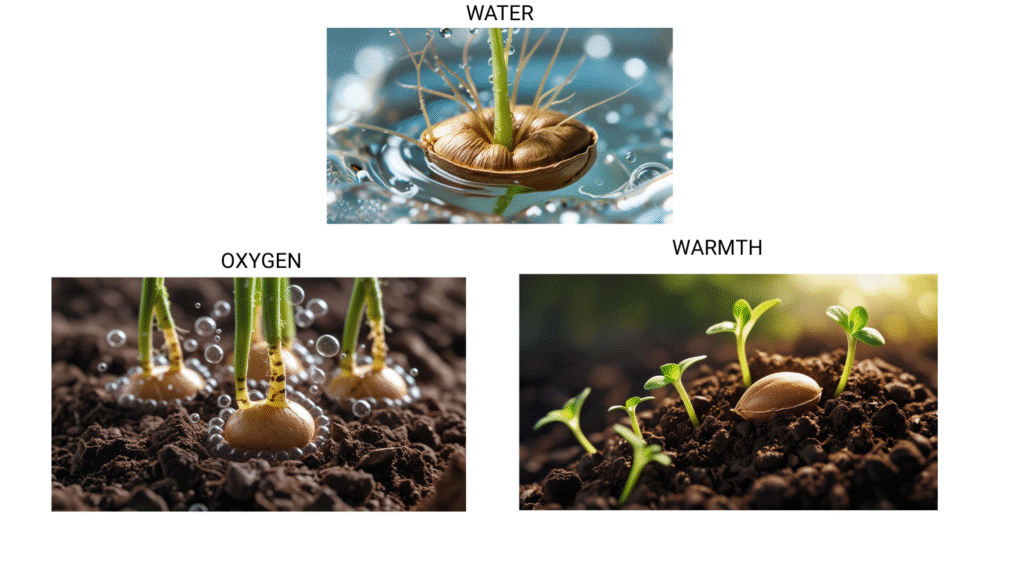
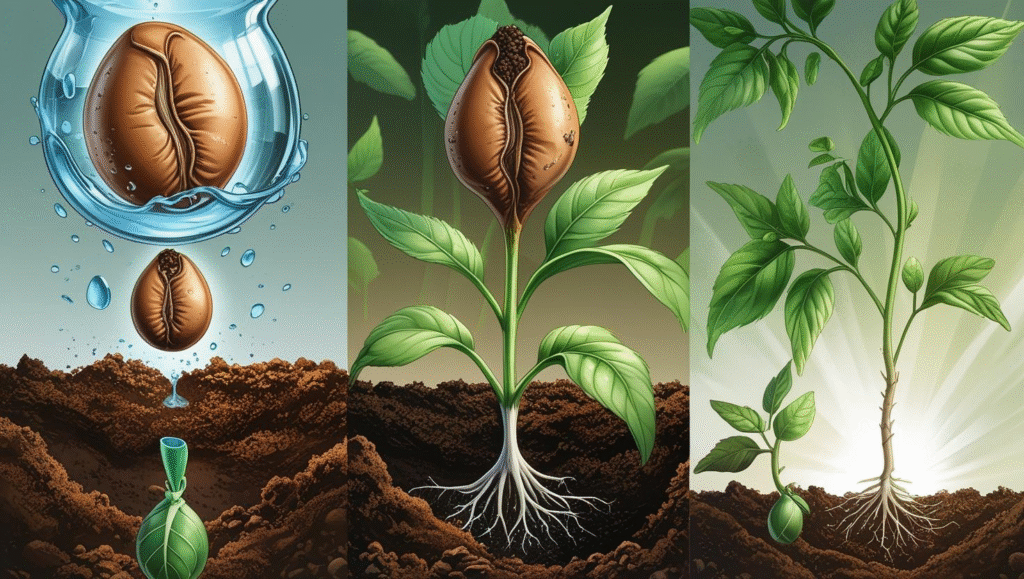
Steps of Germination
- Water Absorption: The seed absorbs water and swells.
- Breaking of the Seed Coat: The seed coat breaks open, allowing the embryo to grow.
- Growth of the Radicle: The radicle, or the embryonic root, emerges first and grows downward into the soil.
- Shoot Emergence: The shoot, which contains the stem and leaves, grows upward towards the light.

Types of Seeds
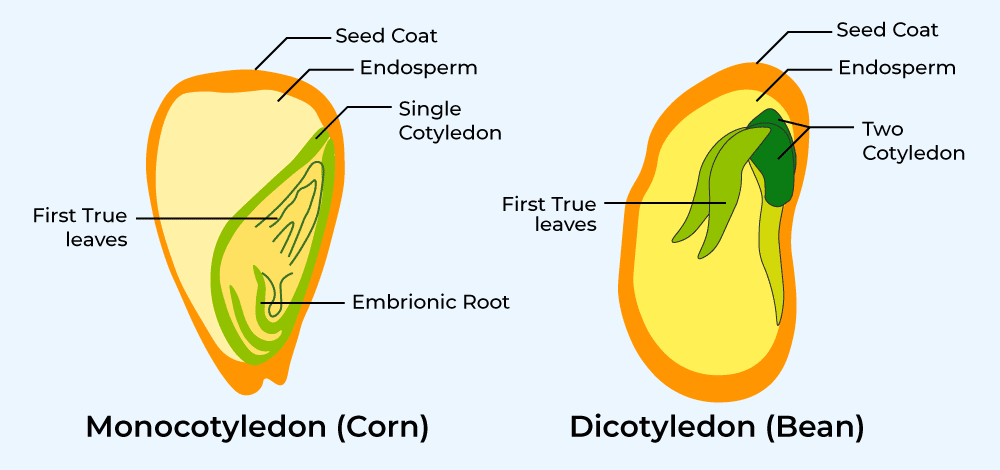
- Monocotyledons (Monocots): Seeds with one cotyledon (e.g., wheat, corn).
- Dicotyledons (Dicots): Seeds with two cotyledons (e.g., beans, peas).
Seed Dispersal
- Importance: Prevents overcrowding and ensures that plants can grow in different areas.

Methods of Seed Dispersal:
- Wind Dispersal: Seeds are light and have wings or fluff (e.g., dandelion).
- Water Dispersal: Seeds float and are carried by water (e.g., coconut).
- Animal Dispersal: Seeds are carried by animals, either by attaching to fur or being eaten and excreted (e.g., berries).
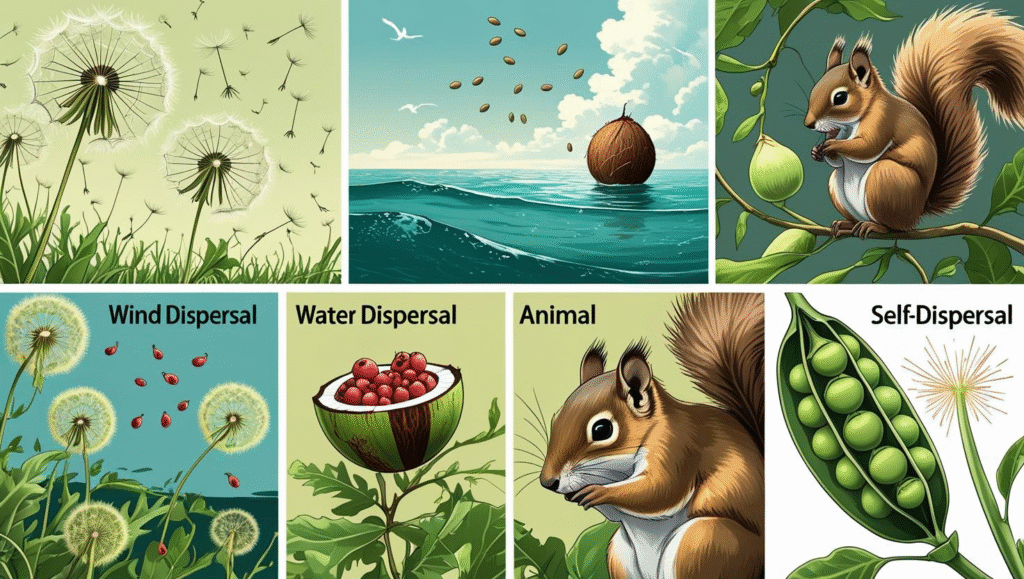
Self-Dispersal: Some plants eject their seeds forcefully (e.g., peas).
Importance of Seeds
- Food Source: Seeds are a primary food source for humans and animals (e.g., grains, nuts).
- Plant Survival: Seeds ensure the survival of plant species by allowing plants to reproduce and spread.

Seed Conservation
- Seed Banks: Facilities that store seeds to preserve plant diversity and protect against loss of plant species.

Let’s practice!

