Dispersal of Seeds
Key notes :
What is Seed Dispersal?

- Definition: Seed dispersal is the process by which seeds are spread away from the parent plant to reduce competition and increase the chances of survival.
- Importance: It ensures that seeds grow in favorable conditions and helps plants to colonize new areas.
Methods of Seed Dispersal

Seeds can be dispersed through various methods:
Wind Dispersal:
- Seeds are light and may have wings or hair-like structures that help them float in the air.
- Examples: Dandelion, Maple.
Water Dispersal:
- Seeds can float and are carried away by water currents.
- Examples: Coconut, Water Lily.
Animal Dispersal:
- Seeds stick to the fur or skin of animals, or are eaten and later excreted in a different location.
- Examples: Burdock, Berries.
Explosive Dispersal:
- Some plants have seed pods that burst open forcefully, scattering seeds in various directions.
- Examples: Peas, Touch-me-not (Impatiens).
Gravity Dispersal:
- Seeds fall directly to the ground due to gravity, often rolling away from the parent plant.
- Examples: Apples, Nuts.
Adaptations for Dispersal
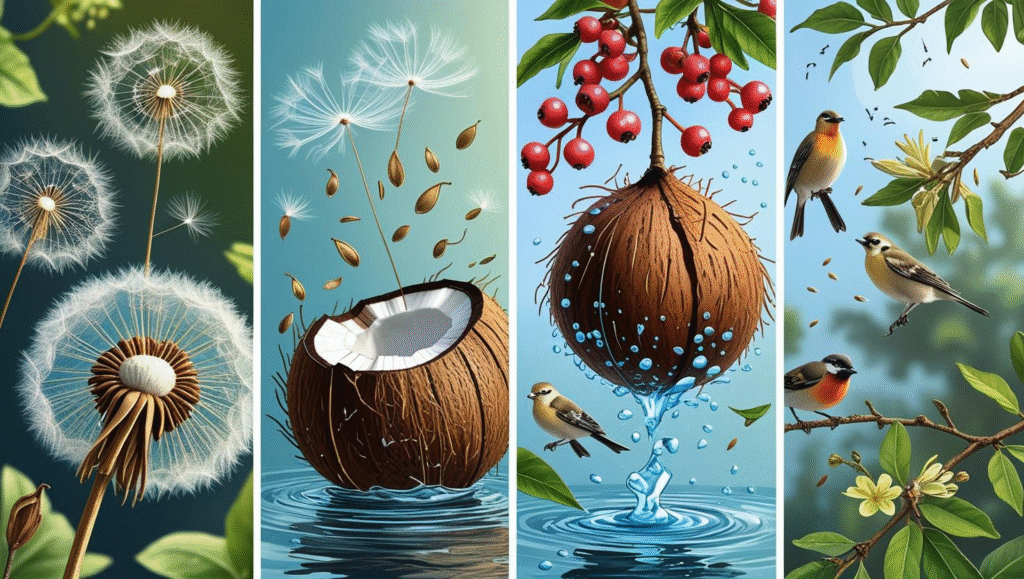

- Wind: Seeds are lightweight, have wings or parachutes (e.g., dandelions).
- Water: Seeds are buoyant, allowing them to float (e.g., coconut).
- Animals: Seeds are sticky or enclosed in fruit that attracts animals (e.g., burrs, berries).
- Explosive: Seed pods are designed to burst open when mature (e.g., touch-me-not).
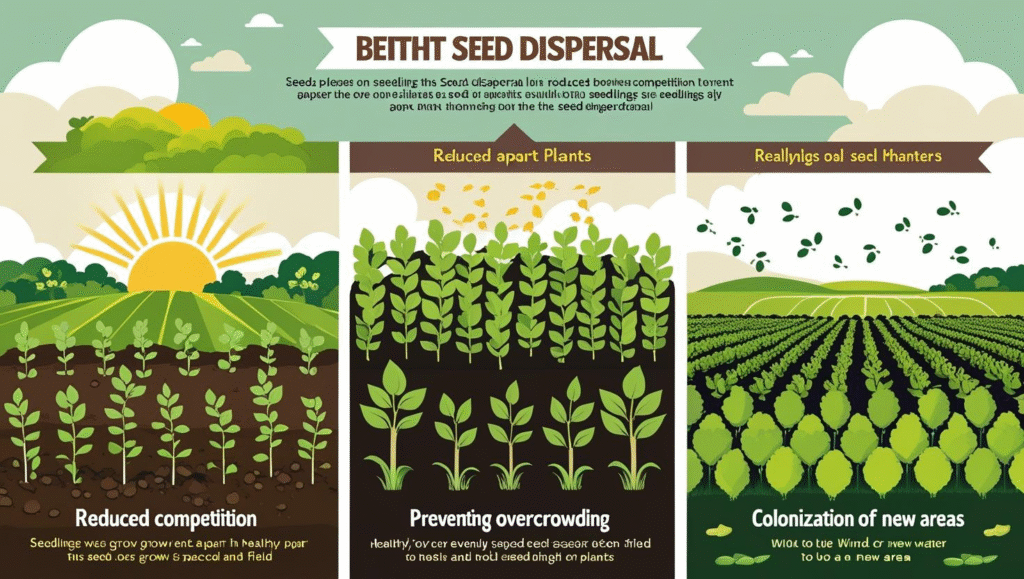
Benefits of Seed Dispersal
- Reduces Competition: Seeds grow away from the parent plant, reducing competition for sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Prevents Overcrowding: Helps in spreading out plants, leading to better survival chances.
- Colonization of New Areas: Allows plants to grow in new, potentially favorable environments.
Conclusion
- Seed dispersal is a crucial process for plant survival, enabling them to spread across diverse environments and ensuring the continuity of plant species.
Let’s practice!

