Nerves
nerves by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Definition of Nerves:
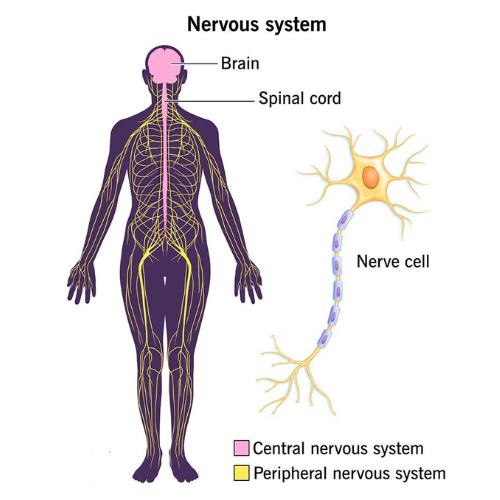
- Nerves are bundles of fibers that carry messages between the brain and other parts of the body. These messages help us move, feel, and respond to the environment.
Types of Nerves:
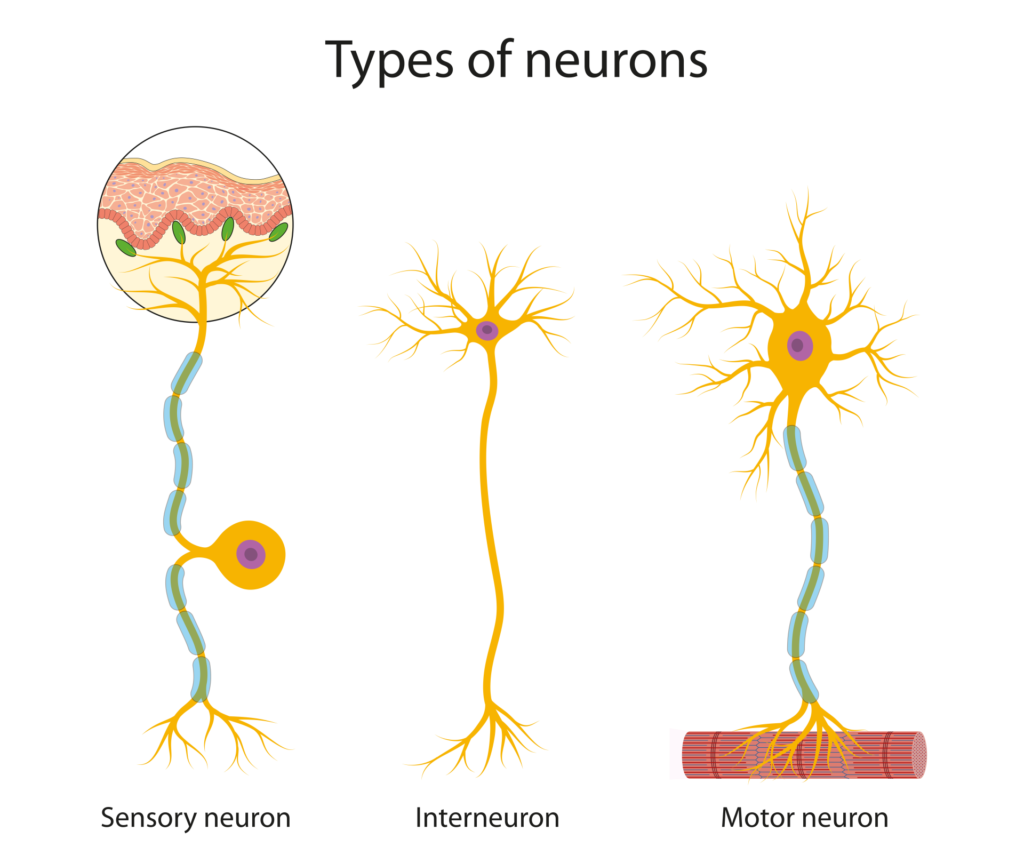
- Sensory Nerves: These nerves carry signals from the senses (eyes, ears, skin) to the brain, helping us understand the world around us.
- Motor Nerves: These carry signals from the brain to muscles, allowing us to move.
- Mixed Nerves: These nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers, so they can send and receive signals.
How Nerves Work:
- Nerves use electrical impulses to transmit information. These impulses travel along the nerve fibers quickly to communicate with the brain and spinal cord.
Parts of a Nerve:
- Neuron: The basic unit of the nervous system, a neuron has a cell body, dendrites (receive signals), and an axon (sends signals).
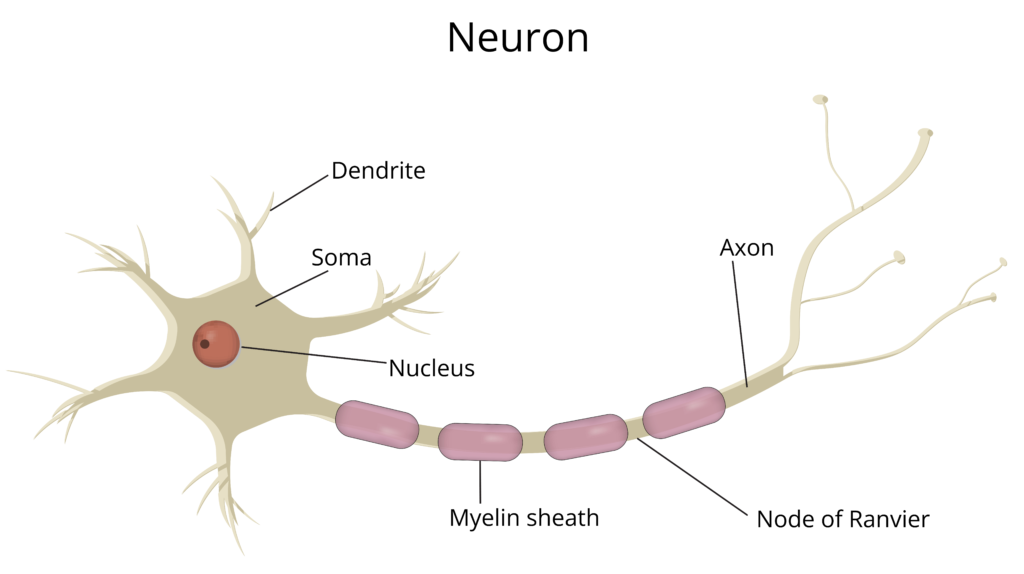
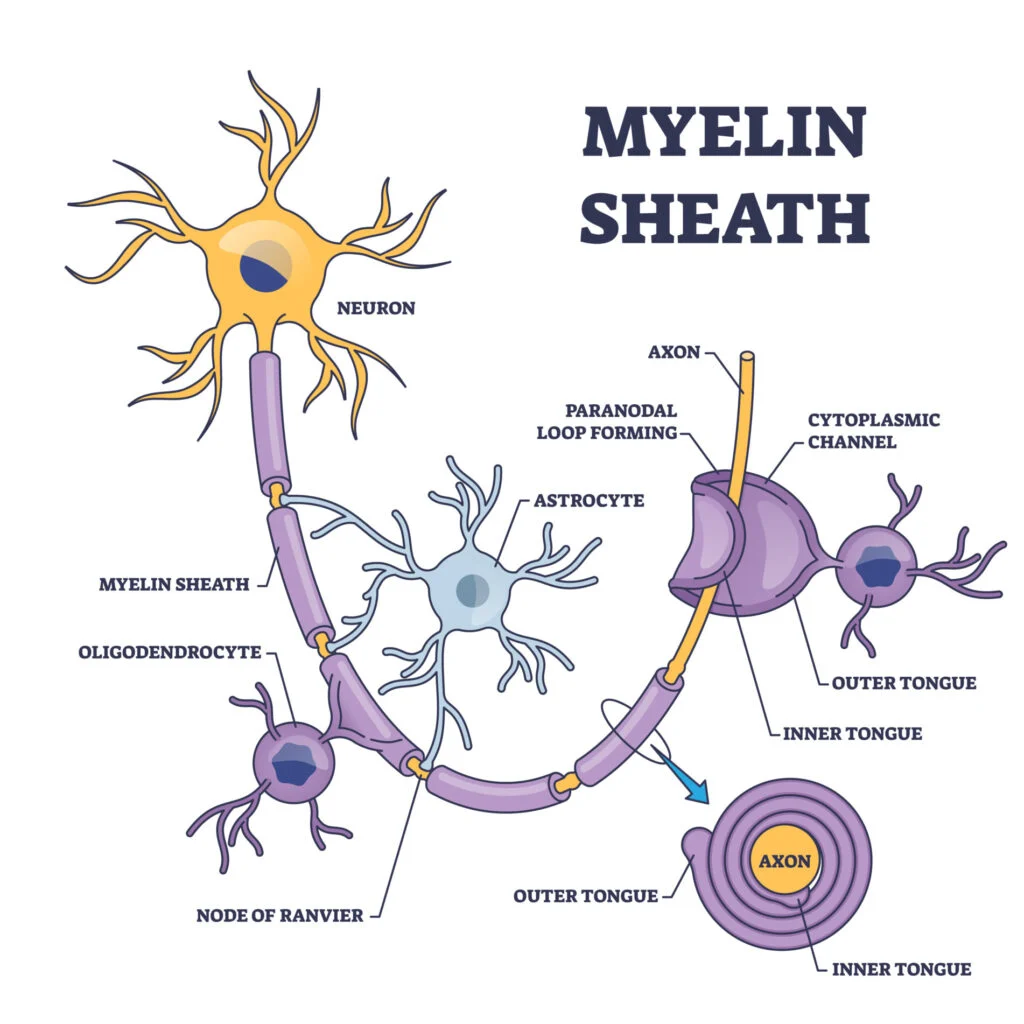
- Myelin Sheath: A protective covering around nerves that helps speed up the transmission of nerve signals.
The Role of the Brain and Spinal Cord:
- The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS), which processes information and controls actions.
- Nerves connected to the CNS are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the rest of the body to the brain and spinal cord.
Importance of Nerves:
- Nerves are essential for controlling bodily functions, such as moving, breathing, feeling sensations, and even digestion.
Common Problems with Nerves:
- Nerve damage or disease can lead to issues such as numbness, pain, or difficulty moving muscles.
Let’s practice!

