Reflex Action
Key Notes:
Definition of Reflex Action:
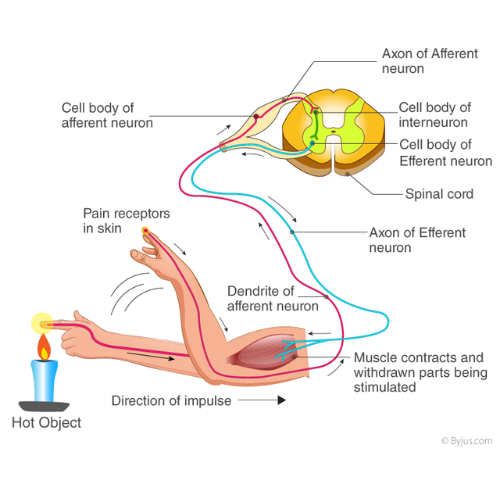
Reflex action is a quick, automatic response to a stimulus without conscious thought. It helps protect the body from harm.
Examples of Reflex Actions:
- Pulling your hand away when touching something hot.
- Blinking when something comes close to your eyes.
- Sneezing when dust enters your nose.
Reflex Arc:
The path that a reflex action takes is called a reflex arc. It involves:
- Stimulus: Something that triggers the reflex (like heat or pain).
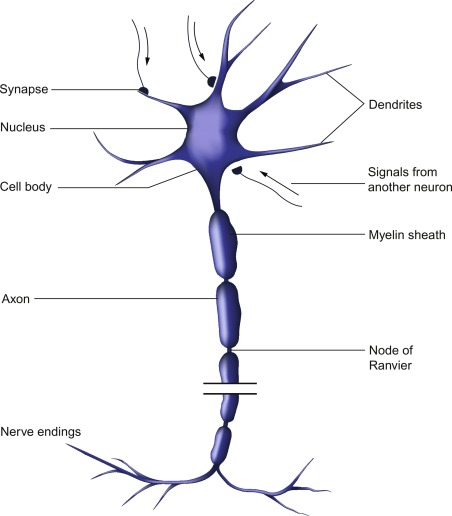
- Sensory Neuron: Carries the message from the body part to the spinal cord.
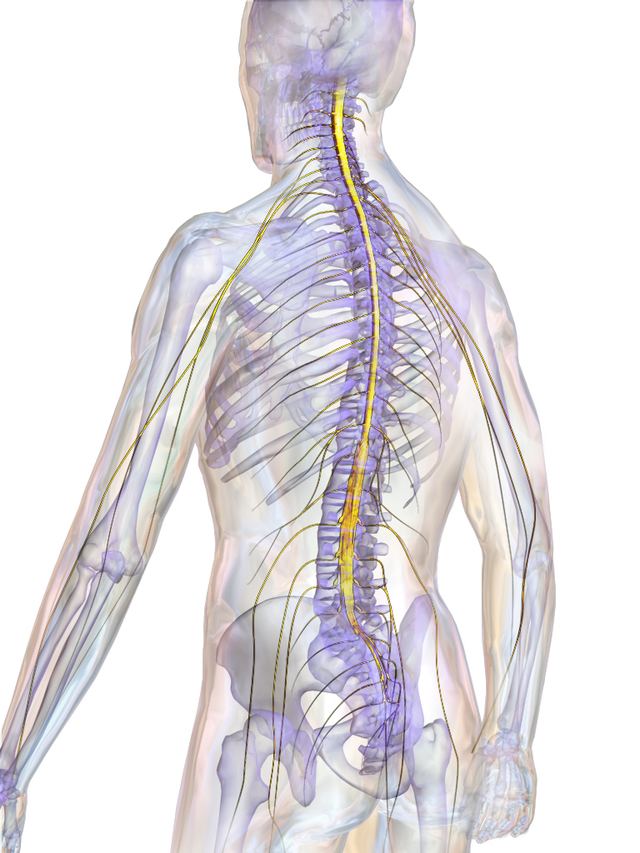
- Spinal Cord: Processes the message and sends a signal back through the motor neuron.
- Motor Neuron: Carries the message from the spinal cord to the muscles to respond.
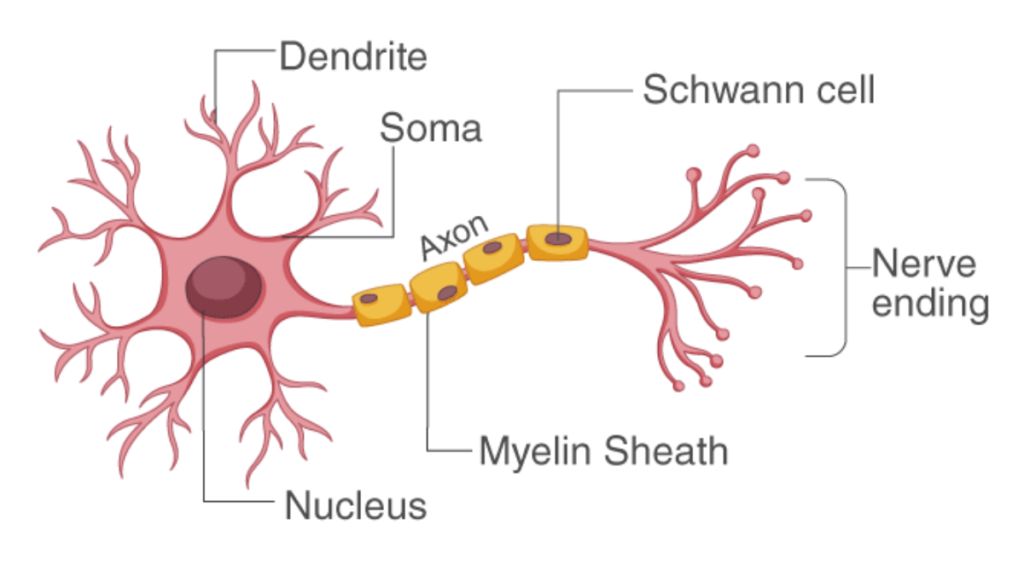
- Effector: The muscle or gland that reacts (like moving your hand).
Types of Reflex Actions: Reflexes can be:
- Natural/Innate: These reflexes we are born with, such as blinking or breathing.
- Learned/Conditioned: Reflexes developed over time, like riding a bicycle.
Importance of Reflex Actions:
Reflex actions protect the body from danger by providing a fast response, ensuring safety before the brain has time to process the situation.
Difference between Voluntary and Reflex Actions:
Reflex actions are automatic and do not involve thinking, while voluntary actions are controlled by the brain and require conscious thought.
Let’s practice!

