The Ears
the ears by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Parts of the Ear:
- Outer Ear: Includes the ear canal and earlobe; it collects sound waves.
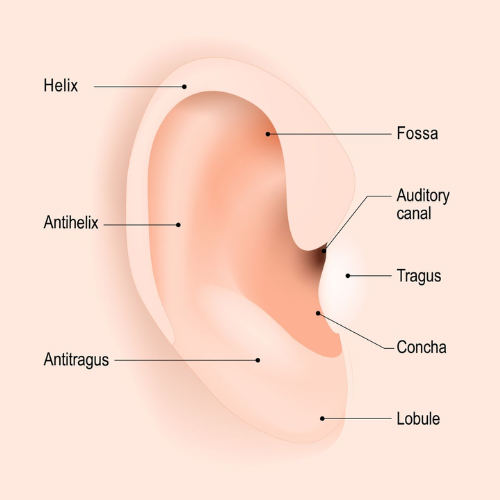
- Middle Ear: Contains the eardrum and three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) that amplify sound vibrations.
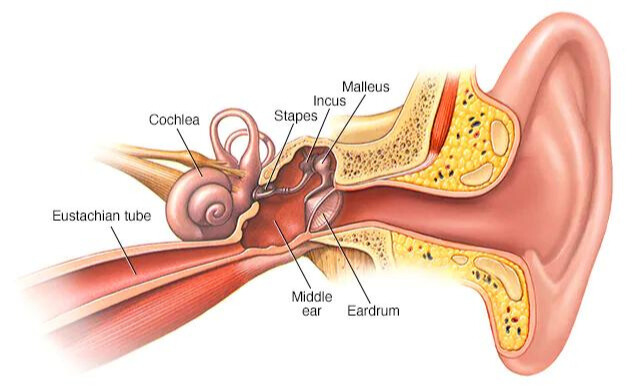
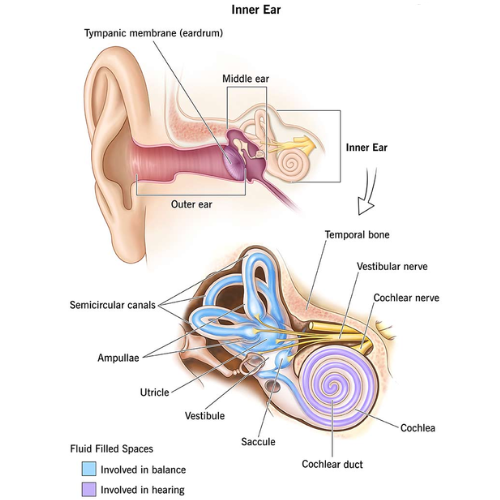
- Inner Ear: Contains the cochlea (which helps with hearing) and the semicircular canals (which help with balance).
How We Hear:
- Sound waves are collected by the outer ear and travel through the ear canal.
- The sound waves make the eardrum vibrate.
- The vibrations are passed through the middle ear bones to the cochlea in the inner ear.
- The cochlea converts vibrations into electrical signals, which are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Function of the Ear:
- Hearing: Ears capture sound waves, convert them into signals, and send them to the brain.
- Balance: The semicircular canals in the inner ear help maintain body balance.
Protecting the Ears:
- Avoid loud noises to protect the eardrums.
- Clean ears gently and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Wear ear protection in noisy environments.
Hearing Loss:
- Causes of hearing loss include exposure to loud sounds, infections, and injuries.
- Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent depending on the damage.
Interesting Facts:
- Ears not only help in hearing but also play a key role in balance.
- Humans can hear sounds in the frequency range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Let’s practice!

