Spread Of Infectious Diseases
spread of infectious diseases by Delta publications
Key Notes:
What Are Infectious Diseases?
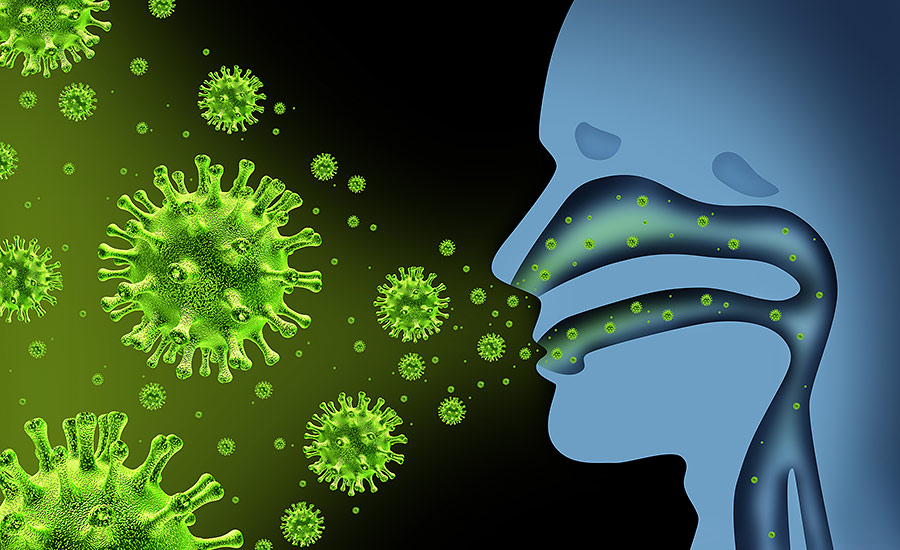
- Definition: Diseases caused by germs (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites) that can spread from one person to another.
- Examples: Flu, cold, chickenpox, and measles.
How Do Infectious Diseases Spread?
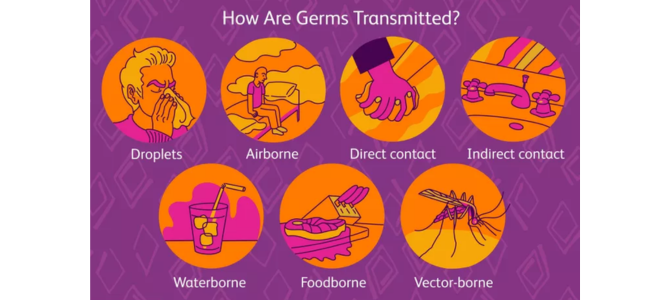
- Direct Contact: Touching or hugging someone who is sick.
- Indirect Contact: Touching objects or surfaces that have germs on them (like doorknobs or toys).
- Airborne: Breathing in germs from coughs or sneezes.
- Food and Water: Eating contaminated food or drinking polluted water.
- Insects: Being bitten by insects that carry germs (like mosquitoes).
Prevention Methods
- Handwashing: Wash hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the restroom.

- Covering Mouth and Nose: Use tissues or elbows to cover coughs and sneezes, and dispose of tissues properly.

- Vaccinations: Get vaccinated to protect against certain infectious diseases.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share food, drinks, or personal items like towels.
- Clean and Disinfect: Regularly clean and disinfect commonly touched surfaces.
Symptoms of Infectious Diseases
- Common Symptoms: Fever, cough, sore throat, rash, or diarrhea.
- When to Seek Help: If you feel very sick or if symptoms persist, it’s important to see a healthcare provider.
The Importance of Hygiene
- Personal Hygiene: Regular handwashing and maintaining cleanliness help prevent the spread of germs.

- Environmental Hygiene: Keeping living spaces clean and free of germs reduces the risk of spreading diseases.

Understanding Germs
- Types of Germs: Learn about different types of germs (bacteria, viruses, fungi) and how they cause illness.
- Germ Lifecycle: How germs can multiply and spread if not properly managed.
Let’s practice!

